-
F8 Last Known Good Configuration Vista
Windows Vista startup process - Wikipedia. This article is about startup process in Windows Vista and later versions. For other uses, see NTLDR.
Windows Vista startup process - Wikipedia. This article is about startup process in Windows Vista and later versions. For other uses, see NTLDR.
The startup process of Windows Vista, Windows Server 2. Windows. In this article, unless otherwise specified, what is said about .
For Windows Vista, the boot sector loads the Windows Boot Manager (a file named BOOTMGR on either the system or the boot partition), accesses the Boot Configuration Data store and uses the information to load the operating system. Then, the BCD invokes the boot loader and in turn proceeds to initiate the Windows kernel. History. It is used by Microsoft's new Windows Boot Manager and replaces the boot. NTLDR. Boot Configuration Data are stored in a data file that has the same format as Windows Registry hives and is eventually mounted at registry key . For UEFI boot, the file is located at \EFI\Microsoft\Boot\BCD on the EFI System Partition. For traditional BIOS boot, the file is at \boot\BCD on the active partition. These menu entries can include: Options to boot Windows Vista and later by invoking winload.
Options to resume Windows Vista and later from hibernation by invoking winresume. Options to boot a prior version of the Windows NT family by invoking its NTLDR. Options to load and to execute a volume boot record. Boot Configuration Data allows for third- party integration, so anyone can implement tools like diagnostics or recovery options.
You can restore your registry files manually to an earlier point by going through the steps outlined below. The process is involved and requires some careful typing. Last Known Good Configuration: Starts the XP system using registry information and drivers that Windows saved at the last shutdown.
Boot loaders. In that respect, winload. NTLDR in prior versions of Windows NT. In UEFI systems, the file is called winload. The only difference is the alternate boot mode and the splash screen displaying . In UEFI systems, the file is called winresume. Advanced Boot Options. Due to the implementation of Hybrid Boot in Windows 8 and up, access to the Advanced Boot Options menu has been disabled by default.
Detect and Fix Drive Errors with Check Disk. Many computer issues are caused by disk corruption or errors on the hard drive, which can be fixed by running the Check.
Reasons Behind Page Fault In Nonpaged Area: Actually, It is tough to identify which program or thing is causing this problem. But, It is quite certain why this. The startup process of Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 and their successors differs from the startup process part of previous versions of Windows.

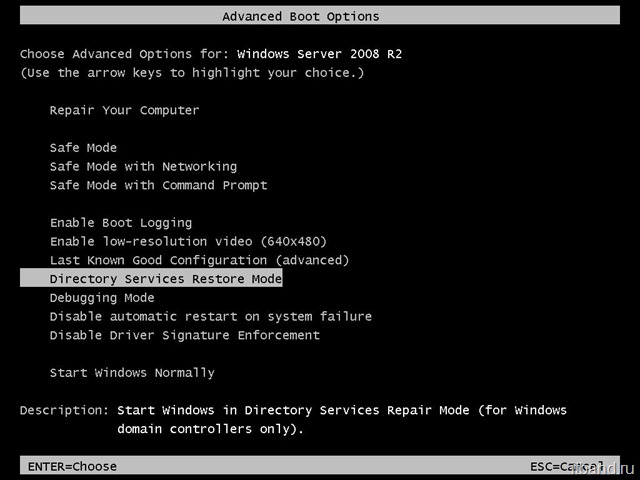
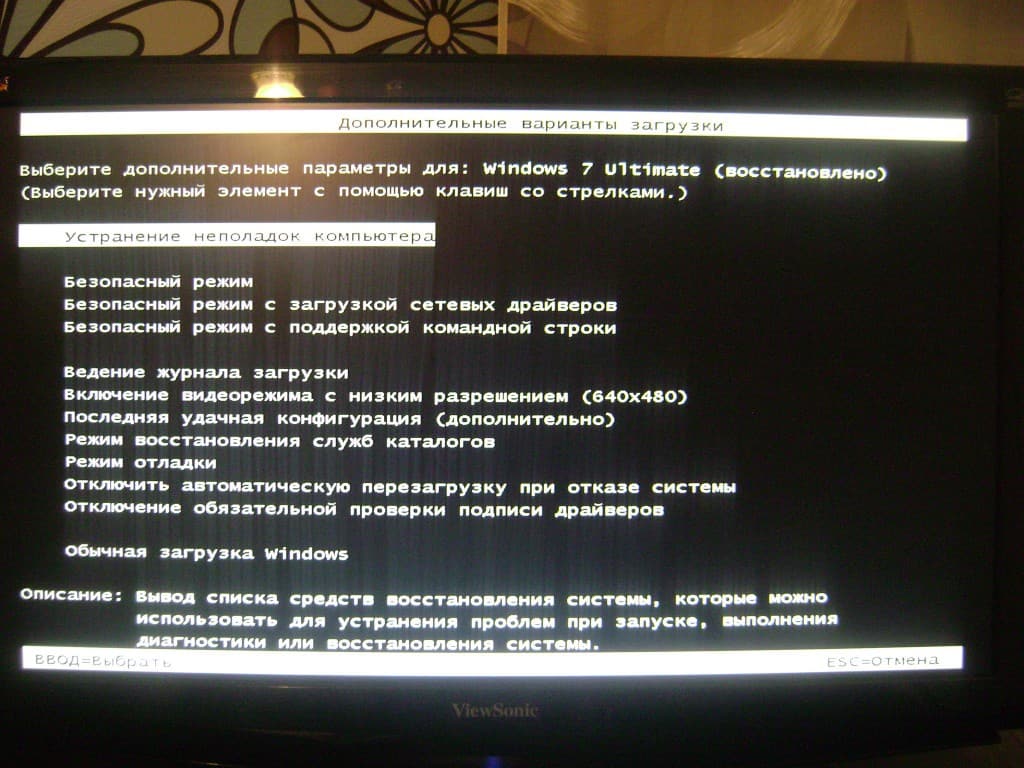
However, access is still possible with a BCD modification. These are the possible boot modes: Repair Your Computer - Boots Windows Recovery Environment (Win.
RE or Windows RE)Safe Mode - Loads Safe Mode, a boot mode with minimal drivers and resources intended for malware removal or replacing faulty drivers. Safe Mode with Networking - Loads Safe Mode along with the network drivers. Safe Mode with Command Prompt - Loads Safe Mode with the Command Prompt as the shell instead of Windows Explorer. Windows Explorer can still be loaded by typing explorer at the command prompt. Enable Boot Logging - Enables writing of ntbtlog.
Enable low resolution video - Disables the default graphics driver and uses the standard VGA driver. Intended in case the user changed the resolution to an unusable level (i. Intended for Registry corruptions. This mode is removed in Windows 8 and later.
Directory Services Restore Mode - Boot mode used to reboot the Domain Controller in case it is not working as intended. Debugging Mode - Boots while loading the kernel debugger.
Disable automatic restart on system failure - Disables the auto- reboot function after a Blue Screen of Death is experienced. Disable early launch anti- malware driver - Allows malware- infected drivers to be loaded. Disable Driver Signature Enforcement - Disables the kernel setting that prohibits unsigned drivers from loading. Start Windows Normally.
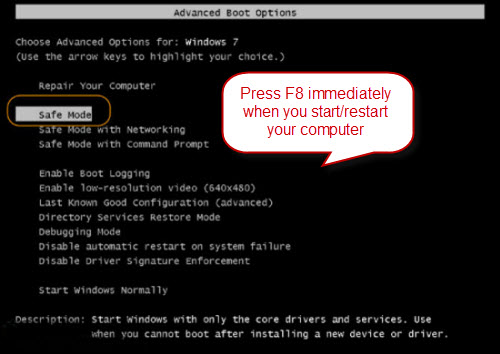
The ABO menu is accessible by pressing rapidly or holding the F8 key before Windows boots.
How to Restart Windows in Safe Mode. Need to get into Safe Mode on your Windows PC? If you’re not able to boot your computer normally, you can try to enter safe mode, a diagnostic mode for Windows that lets you troubleshoot problems that prevent normal booting.
In Safe Mode, Windows only loads the most essential services and drivers in order for it to run. All other normal Windows settings and start up programs are disabled in order to allow the user to fix the problem with their computer. In this guide, I am going to go through the steps to get into Safe Mode in Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8.
Windows 1. 0. Note that if you installed a driver or just recently made a configuration change to your computer, you may want to try the “Last Known Good Configuration” before going into safe mode in Windows 7, Vista and XP. Last Known Good Configuration loads the last working version of Windows. However, it is replaced each time you log into the computer, so if a problem has occurred, make sure to try this option BEFORE logging onto the computer again.
In Windows 8 and Windows 1. Last Known option is no longer included. Instead, they have other options like Refresh, Reset (Reinstall), Restore, etc. I’ll go into more details below in the Windows 8/1. Also note that there are three types of Safe Mode, so read the descriptions below to figure out which one is best for you. Safe Mode – The basic option that loads Windows with a GUI interface and is usually what most people should choose when troubleshooting their computer. Safe Mode with Networking – If you need access to the Internet or the network while in Safe mode, then this is the option to choose.
This mode is useful when you need to fix a problem that requires an Internet connection so that you can download updates, drivers, or other files to help fix your problem. Safe Mode with Command Prompt – This mode will load with just the MS DOS command line prompt. This is useful if you need to run a DOS command like fixboot or chkdsk. Safe Mode in Windows XP/Vista/7. To get into the Safe Mode in Windows XP, Vista or 7, re- boot the computer and then press and hold the “F8 Key” which will then bring up the “Windows Advanced Options Menu“. Scroll down to “Safe Mode” using the arrow keys and press Enter.
Note that sometimes if you press and hold the F8 key, some computers will start to beep annoyingly, so in that case, simply hold the F8 key continuously during the boot up period. If you are still not able to get into Safe Mode, you can try to kill the power on the computer to turn it off and then turn it back on. If Windows shuts down unexpectedly, it will usually bring up the Advanced Boot Options menu automatically. If that doesn’t work, you can read my previous post on getting into Safe Mode if F8 is not working.
This method, however, requires you to be able to log into Windows in order to tell it to boot into safe mode on the next restart. Safe Mode in Windows 8/1. In Windows 8 and Windows 1. The F8 key no longer works because the boot process is too fast. The only way to get into safe mode is to boot into System Recovery Options, which is where you can perform various troubleshooting tasks including starting in safe mode.
I’ve already written about how to boot to the Windows 8 System Recovery Options screen, but the process is slightly different for Windows 1. I’ll mention it here. In Windows 1. 0, there are two ways to get to the recovery options screen. Firstly, you can click on the new Start button, which is back again in a different form, and then hold down the SHIFT key and click on the power button. While still holding down the SHIFT key, click on Restart. The other way is the same as Windows 8, but it just looks a bit different. Click on the Start button and then click on Settings as shown above.
This will bring up a new Settings dialog that basically replaces the PC Settings dialog in Windows 8. Here you will click on Update & recovery. Now you’ll see the options to refresh your PC, reinstall everything or restart in advanced startup mode. At this point, the process to get into Safe Mode in Windows 8 or Windows 1. You’ll now see three options: Continue, Troubleshoot and Turn off your PC. Now just follow the instructions on my article on booting to safe mode in Windows 8.
You basically click on Troubleshoot and go from there. Windows 8 and Windows 1. If you have any questions about getting into safe mode on any version of Windows, feel free to post a comment.
-
Commentaires
